Beans are nutrient powerhouses, providing an abundance of essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. They are a great source of plant-based protein, making them an excellent option for vegetarians and vegans. Additionally, beans are rich in antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, which have been linked to numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and are known to support heart health by helping to lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood pressure.
Beans are an incredibly versatile and rewarding crop to grow in your garden. Whether you have a sprawling backyard or a small urban space, these legumes can thrive and offer you a bountiful harvest.

The first step in growing beans is to select the right variety for your garden. There are numerous types of beans to choose from, including:
Bush Beans: Compact and ideal for small spaces, bush beans don’t require support and produce a concentrated harvest over a short period.
Pole Beans: These vining beans need trellises or poles to climb, offering a continuous harvest throughout the season.
Snap Beans: Best for fresh eating, snap beans are known for their tender, crisp pods.
Shell Beans: These beans are allowed to mature in the pod until the seeds are fully developed and are often used for drying and storage.
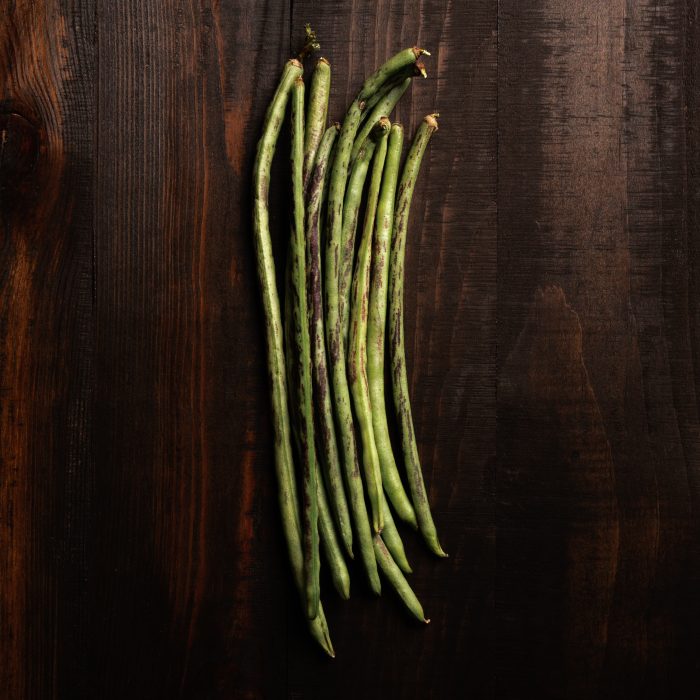
Our favorite beans to grow are Thai Soldier long beans. (shown above) They are fast-growing and tender.
Planting & growing beans
Beans thrive in warm soil, so it’s essential to plant them after the last frost date in your region. Remember to consider your growing conditions and climate when choosing bush beans for your garden, as some varieties may perform better in certain regions. Additionally, it’s a good idea to rotate your bean crops to prevent soil-borne diseases and maintain soil health in your garden.
Select a sunny spot in your garden with well-drained soil. Work organic matter into the soil to improve fertility and drainage. Plant bean seeds about one inch deep and three inches apart in rows. For pole beans, set up supports before sowing. Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged, especially during the germination and flowering stages.
Beans are excellent companion plants, and they can be strategically placed in your garden to benefit other vegetables. They work harmoniously when planted next to crops like corn and potatoes because they can help deter certain pests that affect these plants.
Additionally, beans, with their nitrogen-fixing capabilities, enrich the soil with this essential nutrient, benefiting neighboring plants. However, it’s advisable to avoid planting beans near members of the onion family, such as onions, garlic, and leeks, as they can inhibit bean growth. The same goes for alliums like chives, as these plants may hinder the development of beans.
Harvesting
Harvesting beans is one of the most satisfying aspects of growing them. The timing of the harvest largely depends on the type of beans you are growing.
For snap beans, pick them when the pods are still young and tender, just before the seeds inside begin to swell. Use two hands to gently snap the pods from the plant to avoid damaging the plant.
Blanch and freeze surplus beans to enjoy their garden-fresh flavor throughout the year.
For shell beans, wait until the pods start to fill out and the seeds are plump but not overly mature. When growing dry beans, allow the pods to fully mature and dry on the plant until they turn brittle. To harvest, cut the entire plant, hang it upside down in a dry, well-ventilated area, and thresh the beans from the pods when they are completely dry.
Regular harvesting of snap beans encourages continuous production while being attentive to the right stage for other varieties ensures optimal flavor and quality.
Companion Planting
Beans are excellent companion plants in the garden due to their remarkable ability to benefit neighboring crops in various ways. For instance, beans, particularly bush beans, work well with corn, known as the “Three Sisters” garden. Beans utilize corn as a natural trellis, while their nitrogen-fixing ability enhances soil fertility, benefiting all three crops. Beans also pair effectively with cucumbers, providing a living mulch that conserves moisture and prevents weeds.
Beans can be planted near potatoes, as they repel the Colorado potato beetle, a common potato pest. Companion planting beans not only promotes healthier, more productive crops but also minimizes the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly garden.
Beans enrich your meals with fresh, wholesome flavors while contributing to the health of your garden through their nitrogen-fixing properties. As you nurture your bean plants and savor the fruits of your labor, you’ll not only enhance your culinary creations but also deepen your connection to the beauty and abundance of the natural world, right in your own backyard.
Happy gardening!