When you think of Ohio’s natural beauty, you might picture rolling hills, lush forests, and meandering rivers. But did you know that Ohio is also home to a unique and surprising native plant species?
The Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus (Opuntia humifusa), a hardy and resilient succulent, thrives in the Buckeye State, adding a touch of desert flair to the diverse Ohio landscape.
The Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus, often referred to simply as the “prickly pear,” is a member of the cactus family (Cactaceae) and is native to eastern North America. This cactus species can be found in various states, including Ohio, where it thrives in specific habitats such as dry, sandy soils, and open prairies.
The Eastern Prickly Pear stands out with its distinctive appearance. It typically grows low to the ground, forming flattened, segmented pads or stems covered in formidable spines. These spines, although sharp and prickly, serve as a means of protection from herbivores and excess moisture loss.
While the prickly pear may not seem like a typical flowering plant, it surprises observers with its strikingly beautiful flowers. During the late spring and early summer, this cactus species produces bright yellow to orange blossoms that open in full sunlight. These blooms provide essential nectar for pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Also Read: Autumn Foraging Guide
The Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus plays a crucial role in Ohio’s ecosystem as it creates microhabitats that shelter small animals and insects. These cacti’s pads offer shade, and their presence can help regulate temperature and moisture levels in the surrounding soil.
The vibrant flowers of the prickly pear attract a variety of pollinators, which aids in the reproduction of not only the cactus itself but also other nearby plant species.
The extensive root system of the prickly pear helps stabilize loose, sandy soils. This is particularly important in Ohio, where soil erosion can be a concern in certain areas.
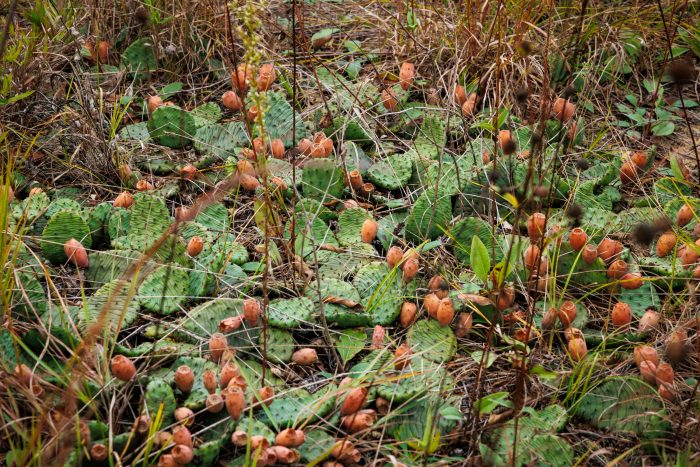

While the Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus is not considered endangered in Ohio, there are still conservation efforts in place to protect its habitat and ensure its survival. Conservationists and organizations work to educate the public about the importance of native species and the role the prickly pear plays in the state’s ecosystems. Efforts also focus on preserving and restoring the cactus’s natural habitat, especially in areas where urbanization threatens local plant life.
Ohio’s native Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus is a remarkable example of the state’s diverse and unique flora. Its ability to thrive in seemingly inhospitable conditions and its importance in Ohio’s ecosystems make it a plant worth celebrating and protecting. So, the next time you’re out exploring Ohio’s natural beauty, keep an eye out for these prickly wonders and appreciate the desert charm they bring to the Buckeye State’s landscapes.

Foraging the Eastern prickly pear
Both the Prickly Pear’s pads (segments) and flowers are edible and have been traditionally consumed by various indigenous cultures and, more recently, by adventurous foragers and culinary enthusiasts.
The pads of the Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus are the most commonly consumed part. After removing the spines and glochids (tiny, hair-like structures) and properly preparing them, the pads can be cooked and eaten. They have a mild, slightly tangy flavor and a texture that can be likened to green beans or bell peppers.
The flowers of the Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus are not only edible but also quite flavorful. When harvested at their prime (fully open), they can be used fresh in salads, steeped to make herbal tea, used in culinary garnishes, or even turned into jellies and syrups.
While the Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus is edible and can be a unique addition to your culinary repertoire, it’s crucial to handle and prepare it correctly to avoid contact with the sharp spines and glochids. Additionally, make sure you’re harvesting from clean and uncontaminated areas and not depleting local populations of this native species. Responsible harvesting and preparation practices are essential for both your safety and the conservation of this valuable plant.