The intricate tapestry of life on our planet thrives on diversity. Within this rich web of species, there exists a group of unsung heroes—creatures that silently toil to sustain the environment. From the tiniest insects to the mightiest mammals, these organisms play critical roles in shaping ecosystems, providing invaluable services, and ensuring the balance of nature.
Many creatures over-winter in fallen leaves, and they play essential roles in the environment by helping with decomposition, and nutrient cycling, and serve as food sources for other animals ultimately contributing to the overall health and balance of the environment.
Why care for Beneficial creatures
Neglecting the welfare of creatures that are beneficial to the environment would have profound and adverse consequences. Without care and attention to their well-being, these creatures face extinction or population decline, leading to imbalances in ecosystems.
The loss of pollinators, for example, would result in decreased crop yields and a heavy reliance on artificial pollination methods, impacting food production and global food security. Neglecting beneficial microorganisms and soil-dwelling organisms would disrupt nutrient cycling, leading to impoverished soils and reduced plant growth. The disappearance of small mammals and birds that help disperse seeds would hinder forest regeneration and diversity. Neglecting these creatures disrupts food webs, potentially causing population declines in predators, which can have cascading effects throughout ecosystems.
Inaction regarding these vital organisms ultimately jeopardizes the health of our environment, threatening the well-being of all life forms, including our own. Thus, caring for these creatures is crucial for the sustainability and balance of our planet.
- Why care for Beneficial creatures
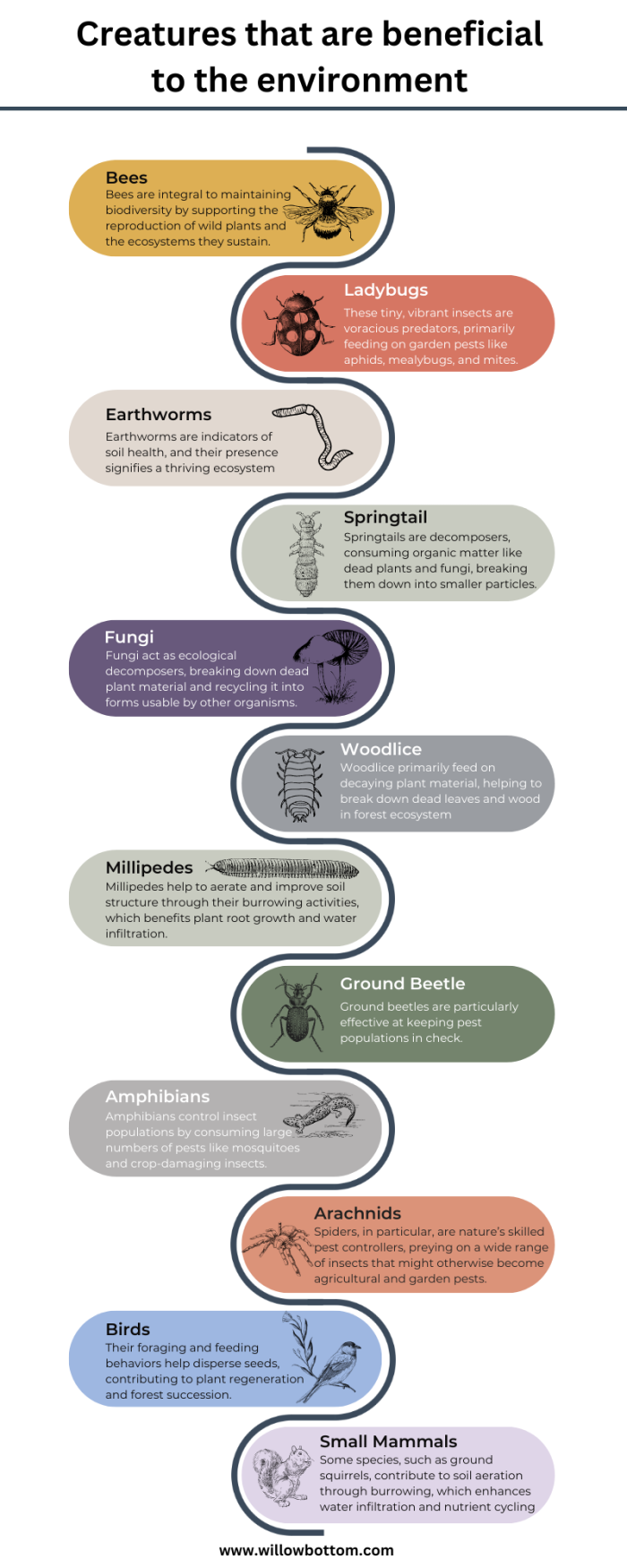
- Bees
- Ladybugs
- Earthworms
- Springtails (Collembola)
- Fungi (e.g., Mycorrhizal fungi)
- Woodlice (Isopods)
- Millipedes
- Ground Beetles
- Amphibians (e.g., salamanders and frogs)
- Arachnids (e.g., spiders)
- Insect Pupae
- Birds
- Microbes (e.g., bacteria and fungi)
- Small Mammals (e.g., shrews and voles)
Bees
Bees, particularly honeybees and native bee species, are indispensable to the environment. They are renowned for their critical role as pollinators, transferring pollen from flower to flower as they collect nectar. This vital service enables the reproduction of countless plant species, including many that provide food for humans and wildlife. Bees contribute to the growth of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and other crops, making them essential to agriculture and global food security.
Beyond pollination, bees are integral to maintaining biodiversity by supporting the reproduction of wild plants and the ecosystems they sustain. Their industrious work enhances both the quantity and quality of the food we eat while playing a vital part in the health and diversity of the environment. Bees exemplify the profound interdependence of all life forms in our world.
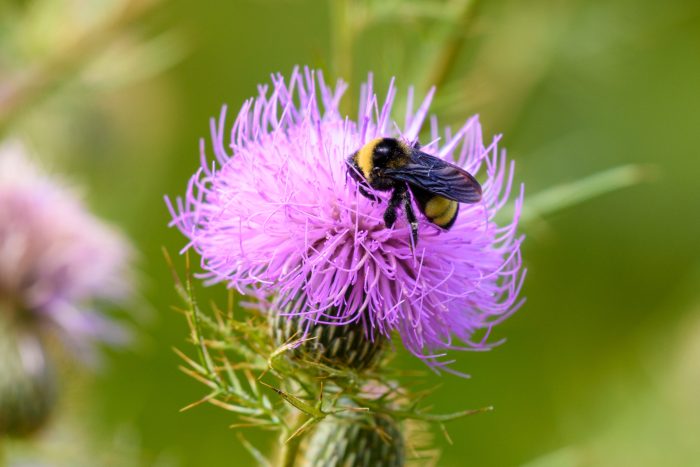

Ladybugs
These tiny, vibrant insects are voracious predators, primarily feeding on garden pests like aphids, mealybugs, and mites. Their appetites make them natural pest controllers, helping to protect crops and ornamental plants. By reducing the need for chemical pesticides, ladybugs promote healthier, more eco-friendly agricultural practices. Moreover, ladybugs are an essential part of the food chain, providing sustenance for various birds and other predators.
Their presence in gardens and natural habitats supports biodiversity and ecological balance. Ladybugs are not only beneficial for controlling pest populations but also for nurturing healthy ecosystems, making them a symbol of the intricate interplay between creatures and the environment.
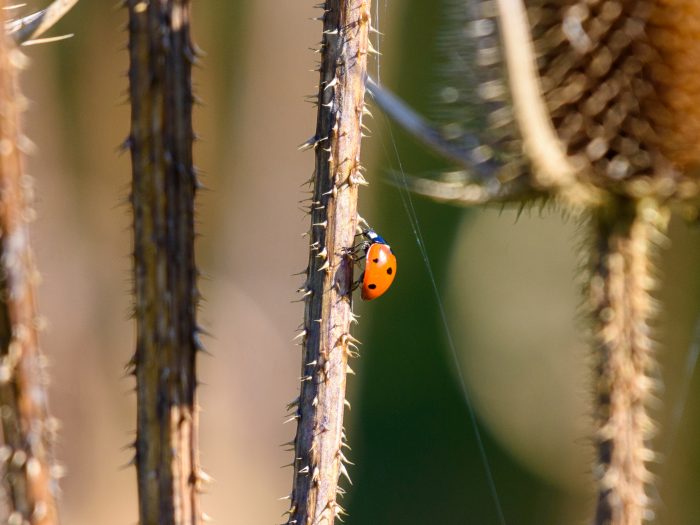

Earthworms
These humble creatures enhance soil structure by burrowing and creating channels for air and water, improving drainage and aeration. As they consume organic matter like fallen leaves and dead plant material, earthworms break it down into nutrient-rich castings, enriching the soil with valuable nutrients and microorganisms. Their tunneling activities also promote root growth and help plants access water and nutrients more effectively.
Earthworms are indicators of soil health, and their presence signifies a thriving ecosystem. Their contributions to the environment extend far beyond their small size, making them essential in sustaining fertile, biodiverse landscapes and supporting the web of life that relies on healthy soil.

Springtails (Collembola)
Springtails, tiny arthropods found in soil and leaf litter, may be inconspicuous, but their ecological significance is immense. They are instrumental in maintaining the health and balance of ecosystems. Springtails are decomposers, consuming organic matter like dead plants and fungi, breaking them down into smaller particles. In doing so, they facilitate the recycling of nutrients back into the soil, benefiting plant growth and the broader food web. These resilient creatures also improve soil structure through their burrowing activities, enhancing aeration and water infiltration.
Additionally, they serve as a vital food source for various soil-dwelling animals, playing a crucial role in the complex web of life below ground. Springtails exemplify the interconnectedness of all living organisms and the importance of even the smallest members of an ecosystem in sustaining environmental health and vitality.
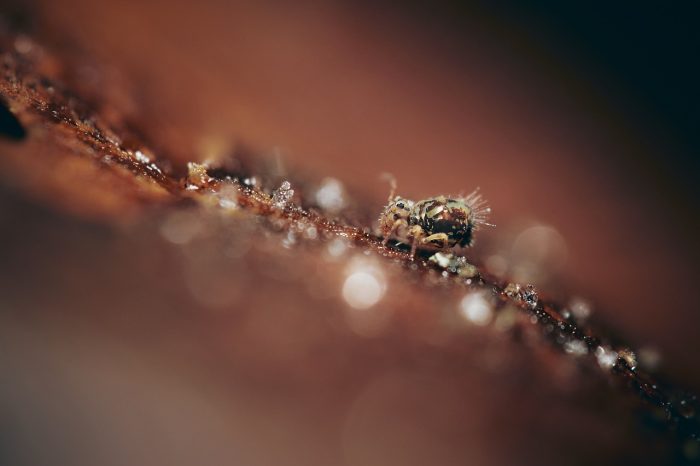

Fungi (e.g., Mycorrhizal fungi)
Fungi are essential and multifaceted contributors to the environment. They play a vital role in nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter and returning essential elements like carbon and nitrogen to the ecosystem. Mycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic relationships with the roots of most plants, aiding in nutrient and water absorption, which is particularly beneficial in nutrient-poor soils.
Fungi also act as ecological decomposers, breaking down dead plant material and recycling it into forms usable by other organisms. Additionally, some fungi have antibiotic properties that help protect plants against diseases. Beyond the soil, mushrooms and other fungi serve as a food source for various wildlife and contribute to biodiversity.

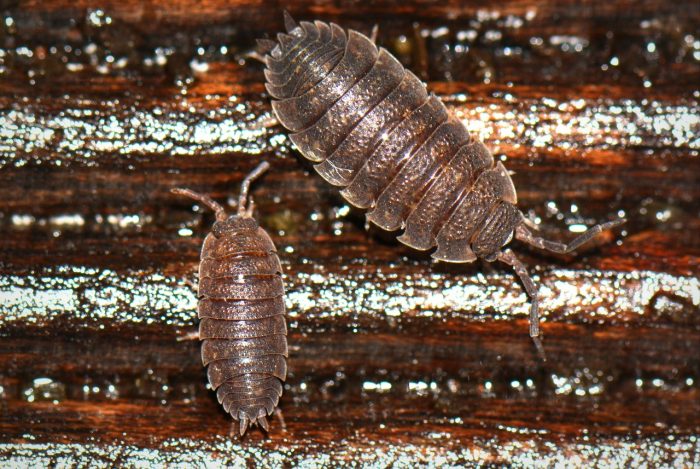
Woodlice (Isopods)
Woodlice, also known as sowbugs or pillbugs, may not receive as much attention as some other creatures, but their role in the environment is vital. These small crustaceans are decomposers that primarily feed on decaying plant material, helping to break down dead leaves and wood in forest ecosystems. By doing so, they contribute to the decomposition process, enriching the soil with valuable organic matter and nutrients.
Woodlice also serve as a food source for various animals, including birds, amphibians, and predatory insects, thus playing a critical role in the food chain. Their presence is an indicator of healthy soil and a well-functioning ecosystem. Woodlice are often unsung heroes, quietly aiding in the recycling of organic matter and promoting environmental sustainability.

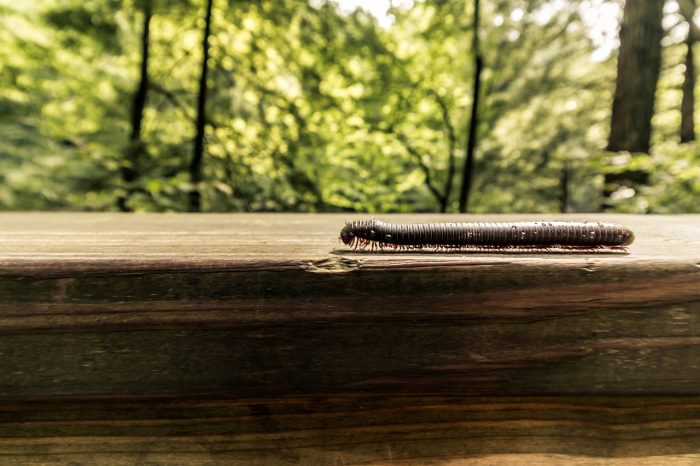
Millipedes
Millipedes, with their numerous legs and segmented bodies, are often misunderstood, but they are valuable contributors to the environment. These detritivores play a crucial role in breaking down decaying plant material, such as dead leaves and wood, into smaller particles. By doing so, they assist in the decomposition process, enriching the soil with organic matter and essential nutrients. Millipedes also help to aerate and improve soil structure through their burrowing activities, which benefits plant root growth and water infiltration.
Additionally, they serve as a food source for various wildlife, including birds and amphibians, further supporting biodiversity. Millipedes may be unassuming, but their role in nutrient cycling and soil health underscores their importance in sustaining healthy ecosystems.

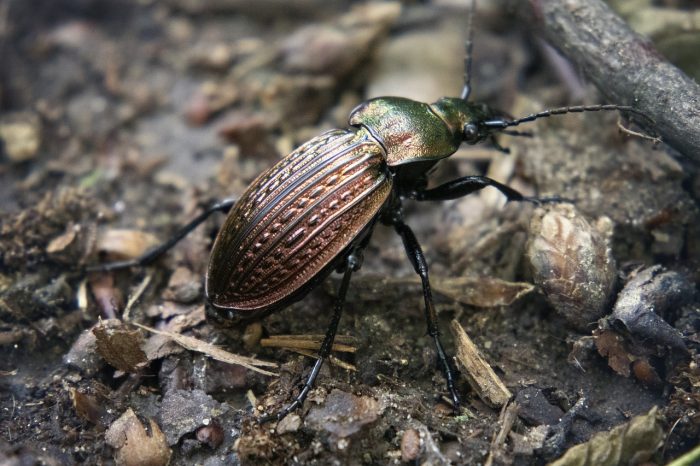
Ground Beetles
Ground beetles are invaluable allies in the natural world, recognized for their essential role in maintaining ecological balance. These predatory insects are voracious consumers of a wide range of garden pests, including slugs, snails, caterpillars, and other insects that can damage crops. Ground beetles are particularly effective at keeping pest populations in check, making them an integral component of integrated pest management in agriculture.
Their nocturnal hunting habits help reduce the need for chemical pesticides and contribute to healthier ecosystems. Beyond pest control, ground beetles also aid in nutrient cycling by consuming organic matter and returning valuable nutrients to the soil. These small, yet formidable, creatures exemplify the vital role of natural predators in promoting biodiversity and ensuring the health of our environment.

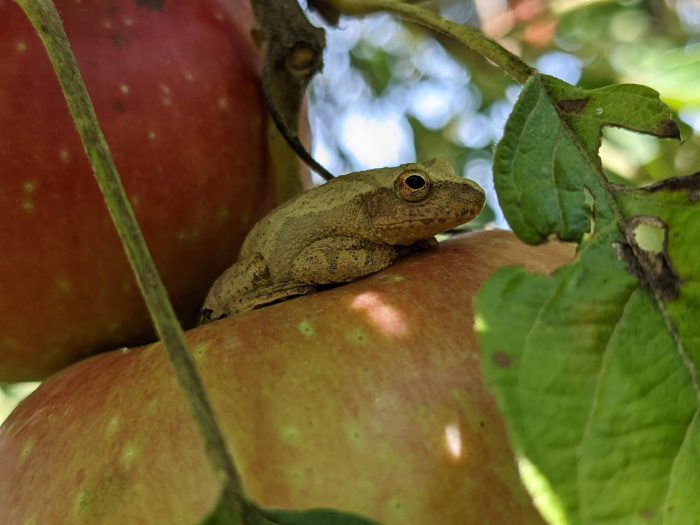
Amphibians (e.g., salamanders and frogs)
Amphibians, including frogs, toads, and salamanders, are essential components of healthy ecosystems, playing multiple critical roles. Firstly, they serve as indicator species, providing valuable insights into environmental health; their sensitivity to environmental changes, such as water quality and habitat conditions, makes them bioindicators for researchers and conservationists. Amphibians also occupy various niches in food webs, both as predators and prey.
They help control insect populations by consuming large numbers of pests like mosquitoes and crop-damaging insects. Additionally, amphibians contribute to nutrient cycling by consuming organic matter and returning essential nutrients to ecosystems, including aquatic and terrestrial environments. Overall, these unique creatures are crucial for maintaining the balance and vitality of ecosystems, and their decline can signal broader ecological imbalances.

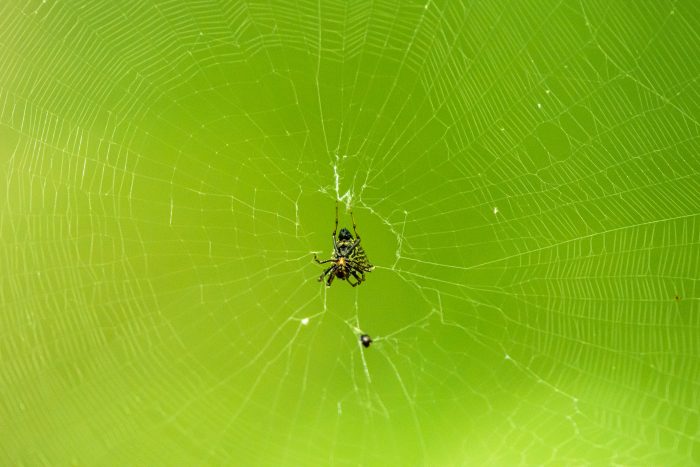
Arachnids (e.g., spiders)
Arachnids, a diverse group that includes spiders, scorpions, and ticks, are indispensable for maintaining environmental balance. Spiders, in particular, are nature’s skilled pest controllers, preying on a wide range of insects that might otherwise become agricultural and garden pests. By keeping these populations in check, they reduce the need for chemical pesticides and help sustain healthy ecosystems. Additionally, arachnids contribute to nutrient cycling by decomposing dead insects and organic matter, returning valuable nutrients to the soil.
They are also a crucial part of the food web, serving as a food source for birds, reptiles, and other predators. While often misunderstood and feared, arachnids are vital players in maintaining ecological harmony and supporting biodiversity in the natural world.

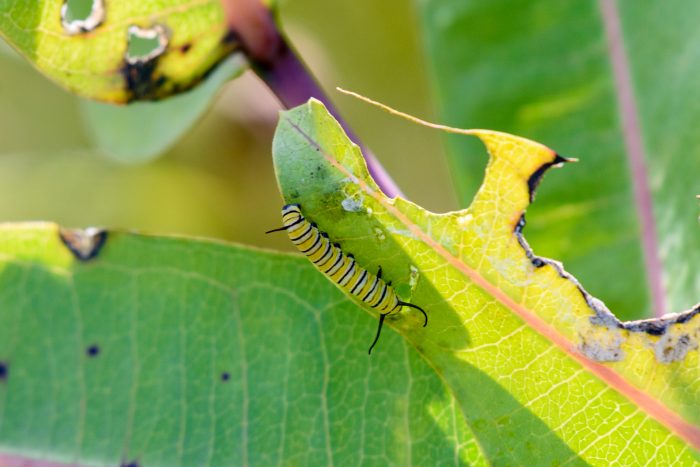
Insect Pupae
Insect pupae represent a stage in the metamorphosis of many insects and serve as vital contributors to environmental health. While in pupal form, insects undergo a transformation from larva to adult, and during this process, they remain largely immobile and vulnerable. This stage is beneficial for the environment as it acts as a buffer against the overpopulation of certain insect species. Insect pupae serve as a form of natural population control, ensuring that insect populations do not become excessive and thereby helping to maintain ecological balance.
By regulating insect numbers, pupae contribute to healthier ecosystems, reduce competition for resources, and play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity. Additionally, they provide essential food sources for various animals, from birds to amphibians, further supporting the intricate web of life in the natural world.

Birds
Birds are integral to the environment, offering a myriad of benefits that extend far beyond their songs and graceful flights. They play a pivotal role in regulating insect populations, serving as natural pest controllers by feeding on various insects, including agricultural and garden pests. Birds are also essential pollinators for many plant species, aiding in the reproduction of diverse flora. Their foraging and feeding behaviors help disperse seeds, contributing to plant regeneration and forest succession. Moreover, birds are a part of complex food chains, with their presence or absence affecting the health of ecosystems.
Their migratory patterns also connect distant habitats, fostering genetic diversity among plant and animal populations. Overall, birds are indispensable for maintaining the balance and vitality of the environment, while their vibrant plumage and melodious calls add beauty and wonder to the natural world.

Microbes (e.g., bacteria and fungi)
Microbes, including bacteria, fungi, and various microorganisms, are the unsung heroes of the environment. These tiny life forms are fundamental to the functioning of ecosystems and the health of our planet. Microbes play critical roles in breaking down organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into valuable nutrients that enrich the soil. This decomposition process, known as nutrient cycling, is essential for plant growth and, by extension, all life on Earth.
Microbes also help purify water by breaking down pollutants and detoxifying contaminants. Additionally, some microorganisms form symbiotic relationships with plants, aiding in nutrient absorption and promoting healthier growth. Microbes are at the heart of biogeochemical cycles, such as the carbon and nitrogen cycles, ensuring the recycling of essential elements. In sum, these microscopic organisms are the invisible architects of our natural world, underpinning the health and vitality of the environment in ways often taken for granted.

Small Mammals (e.g., shrews and voles)
Small mammals, like voles, shrews, and mice, are often underestimated in their significance to the environment. These tiny creatures are essential components of ecosystems, fulfilling various roles that contribute to environmental balance. They serve as prey for many predators, including raptors, snakes, and larger mammals, maintaining a diverse and complex food web.
Small mammals are diligent seed dispersers, helping to regenerate forests and vegetation by spreading seeds in their foraging and nesting activities. Some species, such as ground squirrels, contribute to soil aeration through burrowing, which enhances water infiltration and nutrient cycling. Despite their small size, these mammals are intricate threads in the fabric of nature, playing crucial roles in sustaining biodiversity and ecosystem health.

As stewards of the planet, humans hold a significant responsibility in safeguarding the creatures that are beneficial to the environment. Recognizing and appreciating the vital roles these organisms play in maintaining ecological balance is the first step. We can actively protect them by preserving their natural habitats, reducing pollution and habitat destruction, and supporting conservation efforts. Educating ourselves and future generations about the importance of these creatures fosters an understanding of the intricate relationships in ecosystems.
Practicing sustainable land use, responsible pesticide management and wildlife-friendly gardening promotes coexistence with these beneficial creatures. By embracing our role as protectors of the environment and the creatures that support it, we contribute to a healthier, more biodiverse, and sustainable world for all living beings.
One person can make a difference.